In Total, nearly 54 million people suffer from osteoporosis—a slow attenuation of the bones— that can cause fracture.
In fact 50% of women in the age of 50 or older break a bone owing to osteoporosis. Actually beside osteoporosis is common as smaller toe conditions.
Women usually suffer from osteoporosis more than men, and lack of estrogen during time can enhance the risk of osteoporosis.
But fortunately, In most cases, the low bone density could be prevented. The sooner you begin to visit a foot surgeon in Dubai and take care of your bones healthily, the better you are going to be in the age of 50s and beyond.
What is osteoporosis?
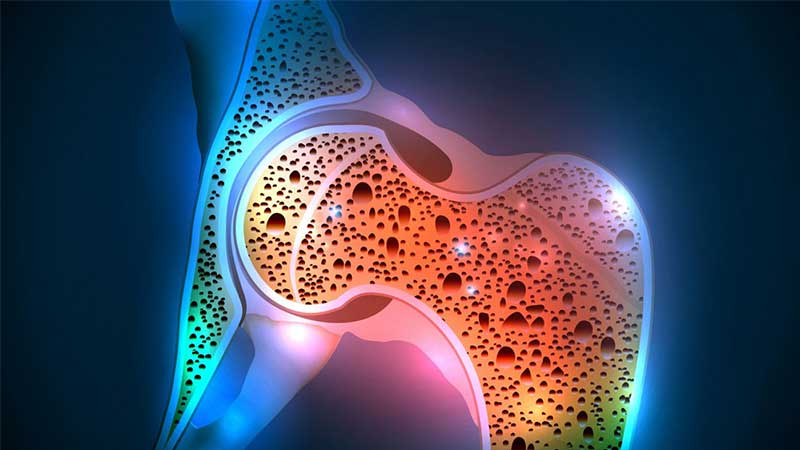
Osteoporosis’ means ‘poriferous bones.’ This disease weakens bones, and people with it are at a serious risk for abrupt and unanticipated bone breaks. In the other word this disease means the patient has less bone pile and strength. Most of the time, it will develop without any signs or pain. As a matter of fact, it is often not detected until the weakened bones lead to painful breaks. Most of the fractures happen to the hip, spine and wrist
According to studies done by a heel surgeon in Dubai, almost 200 million people are calculated to have osteoporosis all over the world. This disease happens in both male and females, but females are four times more likely to be at risk of it than men.
In fact, from the age of 50, one in two females and one in four male could have an osteoporosis-related break in their life cycle.
Osteoporosis causes more than 2 million breaks every year, and this statistic keeps growing.
√ Read more: What is iliotibial band syndrome and what are its symptoms
What causes osteoporosis?
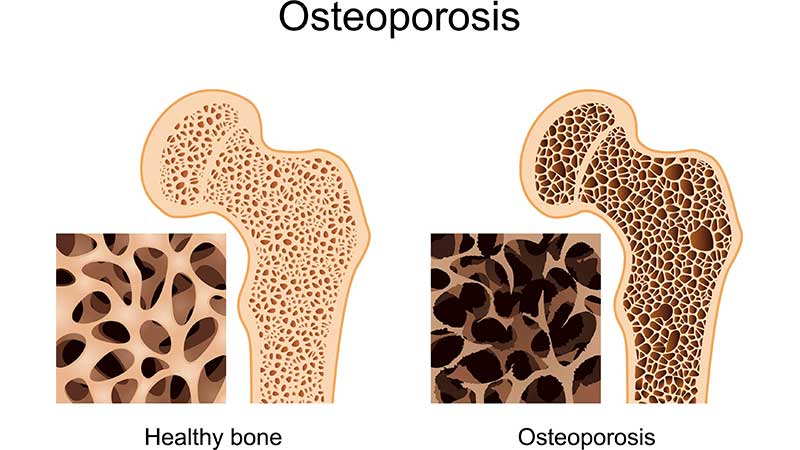
Study results of an ankle surgeon in Dubai show how osteoporosis extends even without being aware of the exact reason of why it extends. The bones are created of vivid and growing tissue. Actually the inside of healthy bones are similar to a sponge that is known as trabecular bone. An exterior peel of compact bone twists around the spongy bone. This tight shell is known as cortical bone.
When osteoporosis happens, the “holes” in the “sponge” become larger and more numerous, which reduces power inside of the bone. Bones protect the body and support vital organs. Bones also save calcium and other minerals. When the body needs calcium, it dialyzes and rebuilds bone. This function, called bone remodeling, prepares the body with needed calcium while keeping the bones strong and together.
Up until about age 30, you normally make more bone than you lose. After age 35, bone breakdown happens faster than bone buildup, which makes a gradual loss of bone mass. If you have osteoporosis, you lose bone mass with a faster speed. After menopause, the speed of the bone breakdown occurs even more quickly.
Complications of osteoporosis
The most dangerous complications of osteoporosis are bone breaks, especially in the vertebral column, ankle or hip. Hip breaks usually are affected by a fall down and could lead to incapacitation and in some situations might enhance risk of death during the first year after the harm.
In some situations, spinal breaks may happen even if the patient hasn’t fallen. In fact this kind of fracture happens because vertebrae weaken to the point of decadence, which could affect back ache, lacking height and a bent forward posture.
In case ankle or heel fractures keep on increasing, osteoporotic surgery might be needed.
Prevent osteoporosis
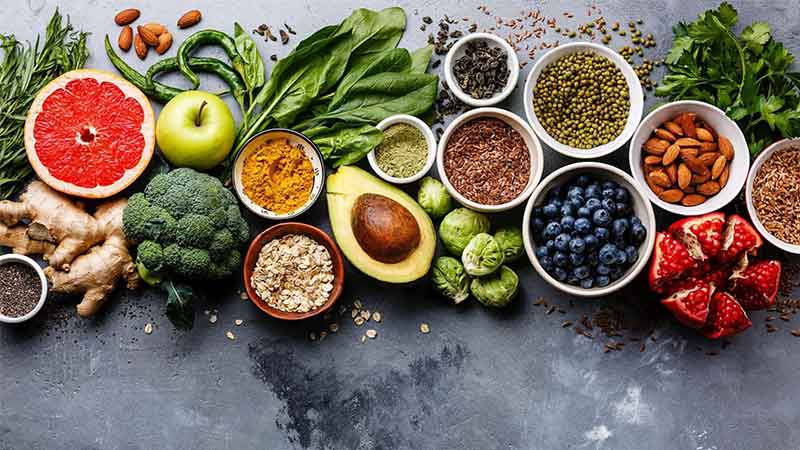

Good nourishment and regular physical exercise are necessary for keeping the bones healthful all over life. The following content includes the ways of prevention of osteoporosis.
Calcium
Both females and males (particularly among the ages of 18 and 50) should consume 1,000 milligrams of calcium every day. This diurnal level enhances to 1,200 milligrams since females turn 50 and males turn 70.
Best sources of calcium:
- Eat low-fat dairy products
- Consume dark green leafy vegetables
- Eat canned salmon or sardines with bones
- Eat soy products, such as tofu
- Consume calcium-fortified, cereals and orange juice
If It’s difficult for you to get enough calcium from your diet, you should take calcium supplements. Anyway, taking more than enough calcium has been linked to kidney stones. Although, some experts say that too much calcium, especially in supplements, can enhance the risk of heart disease.
Vitamin D
Vitamin D recovers the body’s ability to absorb calcium and increase bone health in other ways. People can get some of their vitamin D from sunlight, but this isn’t a good source if you live in a high latitude, if you’re housebound, or if you usually use sunscreen or avoid the sun because of the risk of skin cancer.
Dietary sources of vitamin D consist of cod liver oil, trout and salmon. Many types of milk and cereal have been fulfilled with vitamin D.
Many people need at least 600 international units (IU) of vitamin D a day. This amount increases to 800 IU a day after age 70.
People with limited sun exposure might need a supplement for having IU of vitamin D a day. Most multivitamin supplements include between 600 and 800 IU of vitamin D.
Exercise
Doing exercise can make powerful and strong bones then slow the bone loss process. However, doing exercise is going to benefit the bones no matter when and how you start, you will achieve more benefits in case that you begin exercising customarily, especially at young ages.
Strength training makes the muscles of the arms and spine powerful. Doing weight-bearing exercises like walking, running, skipping rope, … influence the bones in the legs, spine and hip. Finally, balance exercises like tai chi cause reduction of the risk of falling, particularly as you age.
Conclusion
As it mentioned above, osteoporosis is a serious disease that is more likely for females. There are some solutions such as applying vitamin D, calcium, doing exercise and being on a healthy diet can prevent osteoporosis. Furthermore, treatment of this disease includes: taking bisphosphonates, denosumab, bone-building medications, doing hormone therapy, … .
Note: treatment suggestions are according to an estimate of the risk of bone fracture in the future 10 years by applying information such as the bone density examined. In case that risk isn’t extreme, treatment may not include medicines and may concentrate instead on adjusting risk factors.




