An ankle sprain is a very common injury that can occur at any age. This injury usually occurs during exercise, although sometimes it occurs while walking on uneven ground. Sprained ankles occur when the strong ligaments that protect the ankle are overstretched or torn. Sprains can be mild or severe depending on the extent of damage to the ligaments.
Most sprained ankles are minor injuries that improve with home remedies such as rest and applying ice packs. But if your ankle is so swollen and painful that you cannot walk or bear your weight on it, you should definitely see a doctor.
This article will examine ankle sprains, the types of sprains, and their treatment methods.
ٌWhat is an ankle sprain?
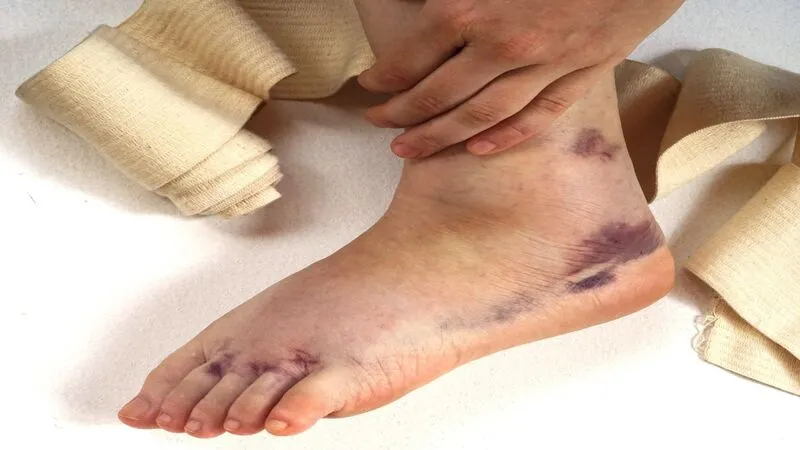
An ankle sprain is a complication in which the soft tissue and ligaments of the ankle are injured and torn. In this situation, the ligament affected the most is the talofibular ligament, which consists of three bands and connects the fibula bone, talus, and heel in the ankle. A ligament is a strong band of connective tissue that connects bones together and keeps them firmly together. The anterior band of the talofibular ligament is injured more than any other ligament in the ankle.
In general, this ligament prevents the strong rotation of the foot and ankle inward. The ligament is torn when the ankle twists strongly inward so that a force greater than the ligament’s tolerance is applied to it. This condition is called an ankle sprain, and its severity can range from a partial and mild tear that results in little pain to a complete tear that results in significant ankle pain and disability.
When you feel pain or see symptoms, you should immediately visit your doctor. Also if you live in Dubai, don’t forget to go for treatment of high ankle sprains in dubai.
✔️ Read More: What is the Avascular Necrosis of the Talus?
The cause of an ankle sprain
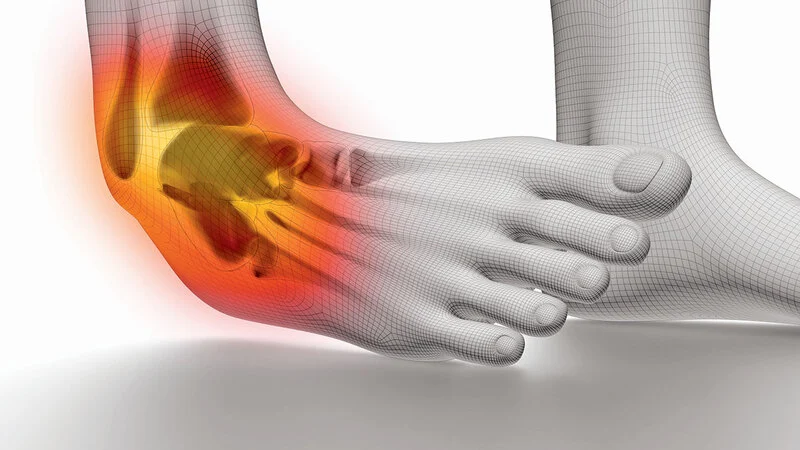
You will most likely get a sprained ankle when your foot turns suddenly. This complication occurs when the sole of the foot moves too far inward. This rotation is called inversion. Excessive twisting can cause the ligaments outside the ankle to stretch beyond their normal limits. Some ligament strands may be torn, or the ligament itself may be completely torn. Sometimes more than one ligament is affected, and sometimes small pieces of bone may be broken.
- Ankle sprains have many causes, including:
- An accident caused by walking on an uneven surface
- A sudden change of direction during exercise
- Unintended landing from a jump
If you have not trained properly or are very inexperienced in a new sport or activity, it is possible to sprain your ankle. You may be more susceptible if you wear the wrong shoes, don’t exercise regularly, or have a medical condition that affects your balance.
If you’ve already sprained your ankle, chances are you’ll do it again. This may be because the ligaments did not heal the first time properly, so they are now weaker.
Symptoms of an ankle sprain
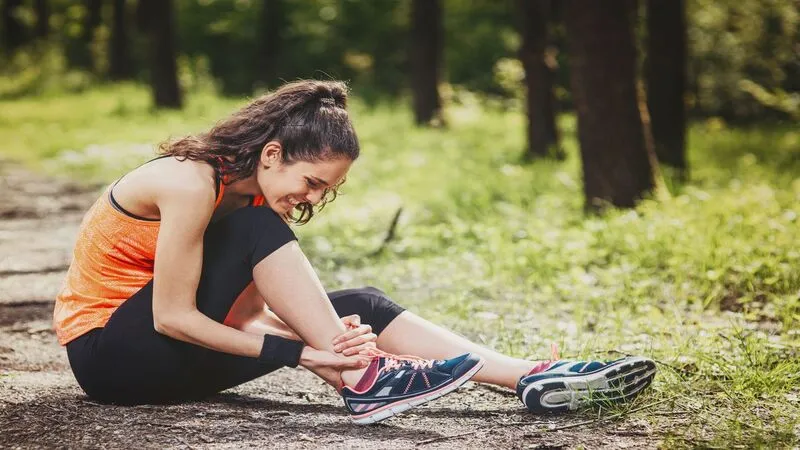

If you see any of the following symptoms in your ankle, you may have a sprained ankle:
- Swelling
- Softening
- A bruise
- The pain
- Inability to bear weight on the injured ankle
- Change in skin color
- Hardness
The ankle can sustain different types of injuries. When you have a problem in the ankle area, it is best to see a doctor because the doctor can determine if the injury to your ankle was a sprain or if you have suffered a more serious injury.
Also, we suggest you prevent all the injuries in childhood since it will reduce treatment in adulthood. Much like an ankle sprain, it’s essential to go for treatment of flat feet in childhood since it will help the child stop any false growth.
✔️ Read More: Ankle instability: everything you need to know about it!
Types and severity of ankle sprains
Sprained ankles are graded based on the degree of damage to the ligaments, which is as follows:
Grade 1 sprain (mild): The ligaments are slightly stretched, and there may be microscopic tears in the ligament fibers. Usually, this type of sprain is accompanied by pain and slight swelling around the ankle. But the person’s range of motion is not affected.
Grade 2 sprain (moderate): ligament fibers are partially torn. Usually, this type of sprain is associated with moderate pain and swelling around the ankle; the person’s range of motion is somewhat reduced, and the joint becomes somewhat unstable.
Grade 3 sprain (severe): Grade 3 sprain is the most severe type of ankle sprain. Ligaments are completely torn, and this is the main cause of joint instability. The person’s range of motion is severely limited.
How to diagnose an ankle sprain?
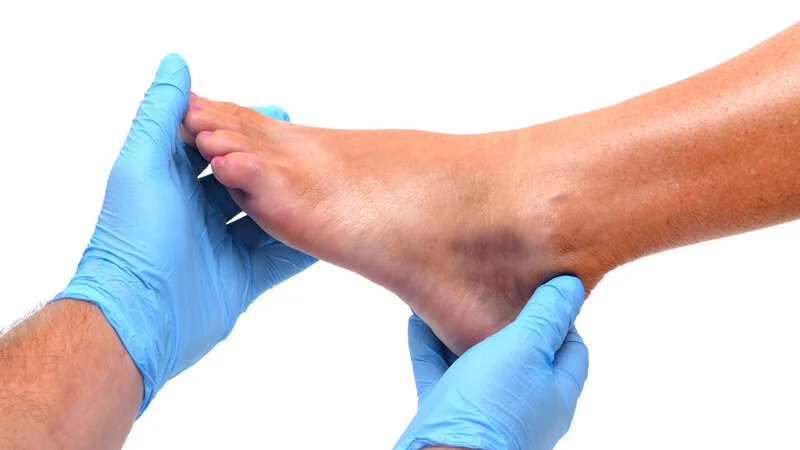
If your symptoms are mild, you may have decided that you have a sprained ankle. Therefore, you can’t seek medical advice. If you are worried about your ankle or if you are in a lot of pain, you can see a doctor.
Your doctor will ask about your symptoms. They will also ask you how exactly you injured your ankle and if you can stand and walk afterward. They may ask you about your medical history and whether you’ve had a similar ankle problem before.
The doctor will examine you, checking for pain, swelling, and bruising around the ankle. They may also check how much you can move your ankle and whether you can put any weight on your foot.
Your doctor can usually diagnose a sprained ankle by listening to what you tell him and examining you. If your doctor thinks your injury is ongoing, you may need some tests, such as X-rays. This is because you may suffer a fracture (broken bone) instead.
Your doctor will usually recommend an X-ray if:
- You cannot walk four steps on your feet
- Your bone (instead of the ligament) is soft
They may also order an ultrasound or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scan to detect if your ankle ligaments are torn or stretched.
✔️ Read More: Bunion Deformity: Everything You Need To Know About It!
Treatment of ankle sprains

Almost all types of sprained ankles can be treated without surgery. Even if the ankle ligament is completely torn, it can be repaired and treated without surgery.
Your doctor may recommend simple home remedies for milder ankle sprains.
RICE protocol
As soon as an injury occurs, follow this protocol:
Rest: Rest your ankle and do nothing during this time. Do not walk with an injured leg.
Ice: Immediately put ice on the ankle so that the swelling does not increase. You should do it 3 to 4 daily for 20-30 minutes. Do not apply ice directly to the skin.
Compression: Use a compression bandage to protect the injured ankle.
Elevation: During the first 48 hours, keep the injured ankle above the level of your heart whenever you can. This helps to reduce or limit swelling. Place your ankle on some pillows to elevate it.
Medicine
Oral anti-inflammatory drugs such as ibuprofen and naproxen reduce the pain and swelling caused by sprained ankles. Due to the reduction of swelling and pain, these drugs are more effective in improving performance than narcotic pain relievers.
Ankle sprains require more treatment than the RICE protocol and medication in more severe cases. Its treatment is much more like the treatment of fractures of the heel bone. You need to go for intense treatment for both of them.
Brace
An ankle brace helps keep the ligaments and joints in place during treatment. The benefits of an ankle brace include limiting movement, preserving the ankle, and reducing pain. The patient may have to wear an ankle brace for 2 to 6 weeks.
Ice therapy
Placing an ice pack on the injured ankle will reduce swelling. On the first day, it is better to put an ice pack on the sprained leg 3 to 4 times during the day for 20 to 30 minutes and use the ice pack once every 3 to 4 hours in the following days.
Splint
The use of a splint significantly improves the problem of sprained ankles very quickly. Since the use of a splint improves the sprain of the foot, reduces the symptoms of the complication, and helps the patient recover the normal function of his body, it significantly affects the treatment of severe ankle sprains.
Stilt
In most cases, swelling and pain last for more than 2-3 days. During this time, walking may be difficult, and your doctor may recommend that you use crutches as needed.
Physiotherapy
Treating sprained ankles with physiotherapy is necessary for all patients with this problem because insufficient rehabilitation leads to inappropriate results and increases the possibility of re-injury. In the absence of proper treatment, sometimes pain and movement disorders of the ankle will bother the person for a long time.
Physiotherapy accelerates the healing process, ensures optimal results, and reduces the likelihood of sprain recurrence. At the same time, it prevents the long-term consequences of an ankle injury. The goals of physical therapy for sprained ankles are as follows:
- Joint protection, pain relief, and inflammation control.
- Full recovery of range of motion
- Leg muscle strength
- Restoring balance
- Restore normal activity
Physiotherapy treatments
Physiotherapy treatment can include the following:
Electrotherapy: helps reduce pain and swelling and increases blood flow.
Ultrasound: Using ultrasound helps to increase the flexibility of tissues and prevent adhesion and the creation of scar tissue.
Soft tissue massage: Usually, scar tissue can be seen in the leg after the damaged ligament heals. Massage therapy prevents the growth of scar tissue during the healing period. With massage therapy, not only does the ankle not lose its flexibility, but the risk of spraining the foot again is reduced.
Manual Therapy: Manual ankle therapy will realign any small bones in the ankle that may have been displaced due to the injury. Suppose the ankle bones are not in their correct anatomical position. In that case, the injured ligament will not heal properly, the ankle will not be structurally stable, ankle arthritis will likely develop, and the ankle will be prone to re-injury.
Shockwave therapy: shockwave therapy by sending shock waves to the tissue in the ankle area causes natural tissue repair so that the new injury caused by the shock is treated and the previous ankle injury is healed.
High-power laser: high-power laser waves increase blood circulation to the damaged point. This mechanism causes the rapid transfer of materials needed to repair the injured ligament and removes the waste materials from the tear in the area.
Dry needling: If the muscles around the ankles are cramped and painful, they can be removed by using a needle.
Exercises
The most important and basic method of treating this disease is to do proper ankle exercises. These exercises improve flexibility, increase muscle strength and endurance, improve balance, and strengthen the sense of proprioception. Each of these movements must be performed under the supervision of a physiotherapist at a specific time. These exercises include the following:
Restoring the range of motion: Swelling and ankle pain limit the ankle’s range of motion. The physiotherapist will teach you how to perform safe and effective exercises to restore the full ankle range of motion.
Muscle strengthening: Wrist muscles weaken after ankle sprains and cause long-term instability of the joint and repeated injuries. Strengthening the muscles of the leg that move the wrist, especially the muscles that rotate the wrist outward, can increase the stability of the ankle. Based on the severity of the injury, the physiotherapist will recommend suitable strengthening exercises for you.
Balance training: special sports movements help your muscles respond appropriately to environmental changes, such as uneven or moving surfaces. Start exercises on the balance board when you can bear weight on your wrists without pain.
Advanced Exercises: Once you can walk comfortably without pain, expand your treatment plan by adding exercises, such as jogging, jumping, or jogging with a change of direction. This program is based on the examination of your ankle by a physiotherapist.
✔️ Read More: Ankle Arthritis; From Diagnosis to Treatment
Surgical treatment
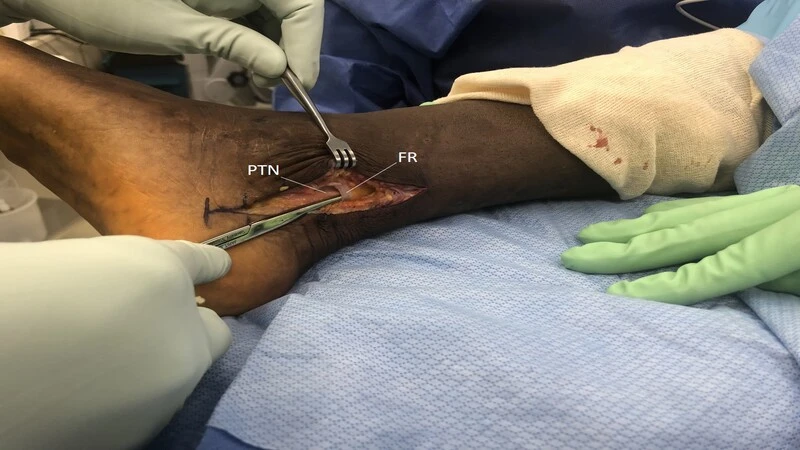
Surgical treatment for ankle sprains is rare. Surgery is performed for injuries that do not respond to non-surgical methods and for patients whose ankle remains unstable after months of rehabilitation and non-surgical treatment.
Surgical options can include the following
Arthroscopy: During arthroscopy, the doctor uses a small camera called an arthroscope to see inside the ankle joint. Small instruments are used to remove any pieces of bone, cartilage, or other parts of the ligament that may be stuck in the joint.
————————–
Rejuvenation: Your doctor can repair torn ligaments with stitches. In some cases, the doctor can restore the damaged ligament by replacing it with grafted tissue obtained from other ligaments or tendons found in the foot and around the ankle.
Immobility: A period of rest and immobility is usually required after surgery. The doctor may apply a cast to the ankle or prescribe the use of protective shoes to protect the regenerated ligament. Follow your doctor’s instructions on how long to wear protective shoes. If you take off that shoe too soon, one wrong step can re-tear the repaired ligament.
Recovery after a sprained ankle

Recovering from a sprained ankle can be frustrating, as it may take several months before you can return to your normal activities. Most ankle sprains heal completely and cause no long-term problems. Your recovery time depends on the severity of your sprained ankle. If you exercise, you may be away from your sports activity for up to six months.
If your sprained ankle is mild (grade 1 sprain), you may be able to walk within the first two weeks after the injury. You should be able to move your ankle fully without any pain within six to eight weeks. You will likely be able to return to exercise within eight to 12 weeks.
On the other hand, if your sprained ankle is moderate (grade 2 sprain), your recovery may take two to three months. You need to be careful because you may re-roll your ankle during the first four to six weeks while you heal. After a while, you may experience some pain and occasional swelling.
A severely sprained ankle (grade 3 sprain) may take several months to heal, and you may even need surgery afterward. Some people with very bad sprains permanently damage their ankles, which may remain unstable (wobbly) and painful.
Treatment results
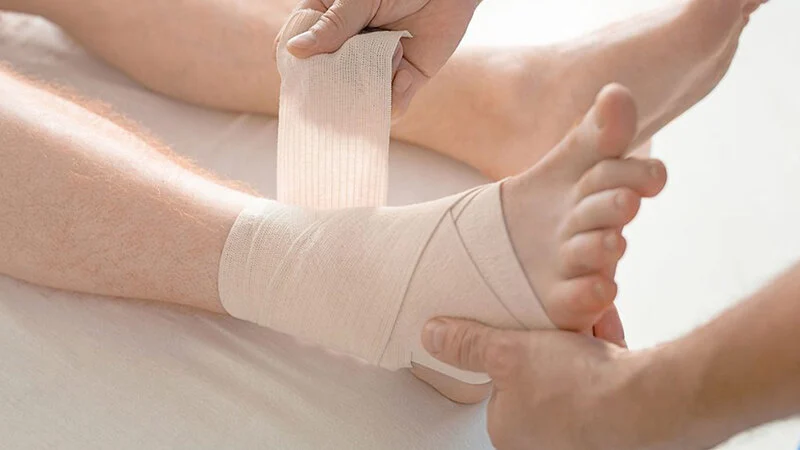
With proper treatment, most patients are able to resume their daily activities after a period of time. It should be noted that successful results depend on the patient’s commitment to rehabilitation exercises. Incomplete rehabilitation is the most common cause of chronic ankle instability after a sprain. If the patient stops strengthening exercises, the affected ligaments will weaken, and the patient is at risk of re-spraining the ankle.
Can a sprained ankle cause permanent damage?
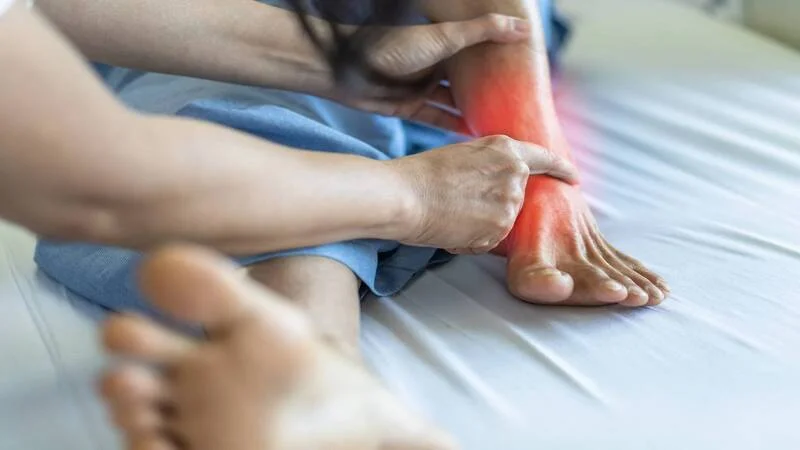
Most people make a full recovery from a sprained ankle. But if your ankle is severely sprained, it can cause permanent damage. If the ligaments haven’t healed properly, your ankle may sprain again.
Long-term problems after an ankle sprain include:
- Chronic pain – pain that lasts a long time
- Chronic instability—when the ankle is unstable for a long time (wobbles when you stand on it)
- muscle weakness
- Occasional ankle swelling
After an injury, it’s important to begin gentle exercises whenever possible to prevent ankle muscle stiffness and keep the ankle moving. Exercise, as well as elastic support, ankle tape, or braces, may help protect the ankle from further sprains.
See your doctor or physical therapist after treatment if your sprained ankle does not improve or your symptoms worsen.
✔️ Read More: What is the Sesamoid Bone? How to Treat it?
How to prevent an ankle sprain?
There are several things you can do to reduce the likelihood of a sprained ankle. These include keeping the muscles around the ankle as strong and flexible as possible. Some other things you can do are listed below.
- Wear shoes that are appropriate for your activity and in good condition. High heels or platform shoes can be dangerous, especially on uneven terrain.
- Take care when walking or running on uneven surfaces—exercise on flat surfaces if you can.
- Before exercising, warm up and stretch your muscles, and then do the finishing exercises and cool down your muscles.
- During certain activities, it may help to wear high shoes (shoes that are higher than the ankle), an ankle brace, or ankle tape.
- Maintain a healthy weight for your height – If you are overweight, you are more likely to sprain your ankle.




