Our bones, muscles, and joints work in unison to keep our bodies moving and stable during movement. Tendons and ligaments also play an important role in performing these movements and maintaining a sitting and standing position. Tendons connect muscles to bones and allow us to move, and ligaments help hold bones in place at the joints. َAlso, the human body has approximately 900 ligaments.
In this article, we want to introduce you to the ligament, its structure, types of ligaments, and the causes of injuries to the ligament. Join us to find the answers to all your questions.
What is a ligament?
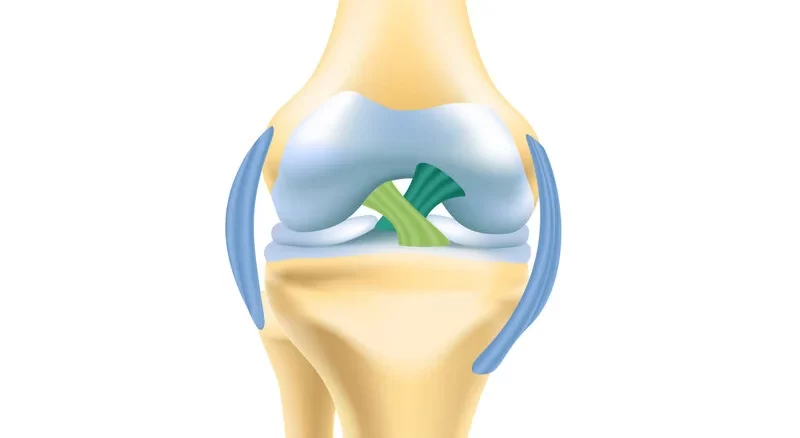
Ligaments are short strips of strong, flexible tissue made up of many single fibers. The ligament has a fibrous structure and is made of connective tissue that has many strong collagen fibers.
Ligaments usually connect two bones, especially at the joints, such as tight bands or ropes, which stabilize the joint or tie the ends of the two bones together. However, some ligaments aren’t attached to the bone. For example, some ligaments hold the internal organs in place. A common example of this is the uterus, which is held in place by the ligaments in the pelvis.
Ligaments come in various shapes and sizes, some of which look like short strands, and some look narrow or wide strips. Also, there are arc-shaped or arched ligaments.
The presence of a ligament ensures that the bones of a joint don’t twist too much, stay close together, and don’t become dislocated. Ligaments may also connect two or more limbs. For example, the liver, intestines, and stomach are held in place by ligaments in the abdominal cavity. These ligaments often have sensitive structures, such as blood vessels or lymphatics, that pass through them. The strong connective tissue of the ligaments protects these structures and prevents them from bending, twisting, or tearing.
Read More: What Is a Tendon? Types of Tendons and the Causes of Their Damage
What is the structure of the ligament?
Skeletal ligaments are dense bands of collagen or fibers that are located at one joint and anchored at both ends of the bone. Different ligaments differ in size, shape, movement direction, and presence.
The unique and complex bone grafts of ligaments are called “linsertions”. Linsertions often have unusual shapes and are located on the bones. These joints are very important in relation to how the ligament fibers work, especially when the joint is moving.
The ligament is seen as a single structure. However, with joint movement, some fibers appear to tighten or loosen depending on the position of the bone and the forces applied.
Read More: Joint peroneal nerve entrapment – diagnosis and treatment
What is the difference between a ligament and a tendon?
The most obvious difference between ligaments and tendons is that the tendons attach the bone to the skeletal muscle, and the ligaments connect the bone to the other bone. Both of these structures have a special type of cell called fibroblasts that forms the structural framework of connective tissues.
Tendons are strong and inflexible, while ligaments are flexible and elastic. Both play a vital role in the joints and bones and are made up of living cells. They also contain a lot of collagen. The important differences between ligaments and tendons are summarized below:
Tendons
- They attach skeletal muscles to bone.
- Tendons are hard and have elastic properties.
- Each head of muscle usually contains a tendon.
- Proteoglycan content is low.
- Its color is white.
- Tendons have poor blood supply.
- Fibroblasts are arranged in a continuous row in tendons.
- The fibers are compact and exist in parallel bundles.
- There is no specific classification for them.
Ligament
- They attach the bones to the bones and are involved in the placement of some organs.
- Elastic and flexible
- They connect the ends of the bones in the joints.
- Each bone has many ligaments.
- The content of proteoglycans is relatively high.
- Its color is yellow.
- Poor blood supply
- Fibroblasts are scattered
- They are not arranged in parallel packages but are packed tightly.
Read More: Examine the causes of flat feet and the best way to treat it!
What are the types of ligaments?
There are different types of ligaments, such as articular, fibrous, and real ligaments. Other ligaments in the body include the “peritoneal ligament,” which is part of the peritoneum or other membranes of the abdominal cavity, and the “fetal remnant ligament,” which are remnants of the fetal placental structure.
The “periodontal ligament” is also a group of fibers that attach tooth cement to the alveolar bone around them, all of which are found in the skeletal system of the human body. Ligaments usually can’t regenerate naturally; however, periodontal ligament stem cells are located near this ligament and are involved in the regeneration of the adult periodontal ligament.
Read More: What does a hammer toe mean and how is it treated?
Types of ligaments in the joints
A ligament usually refers to a group of dense bundles of regular connective tissue made of collagen fibers surrounded by dense, irregular sheaths of connective tissue. Some ligaments restrict joint mobility or prevent certain movements altogether. Capsular ligaments are the parts of the joint capsule that surround the synovial joints and act as mechanical reinforcements. The extracapsular ligaments work together in conjunction with other ligaments to stabilize the joint. In the following, we have introduced the types of joint ligaments.
Knee ligament
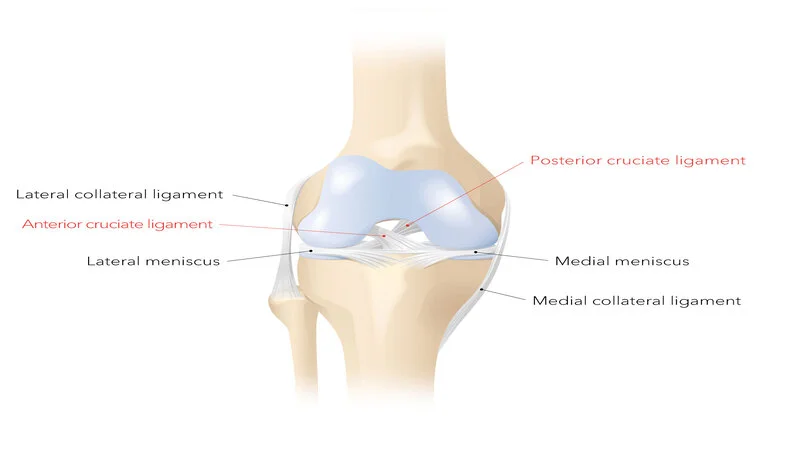
There are four main ligaments in the knee. The ligaments in the knee connect the femur to the tibia (large leg bone) and include the following:
- Anterior cruciate ligament (ACL): This ligament, located in the center of the knee, controls the rotation and forward movement of the large bone.
- Posterior cruciate ligament (PCL): This ligament, in the center of the knee, controls the back movement of the tibia.
- Medial collateral ligament (MCL): A ligament that stabilizes the inside of the knee.
- Lateral Collateral Ligament (LCL): It is a ligament that stabilizes the outside of the knee.
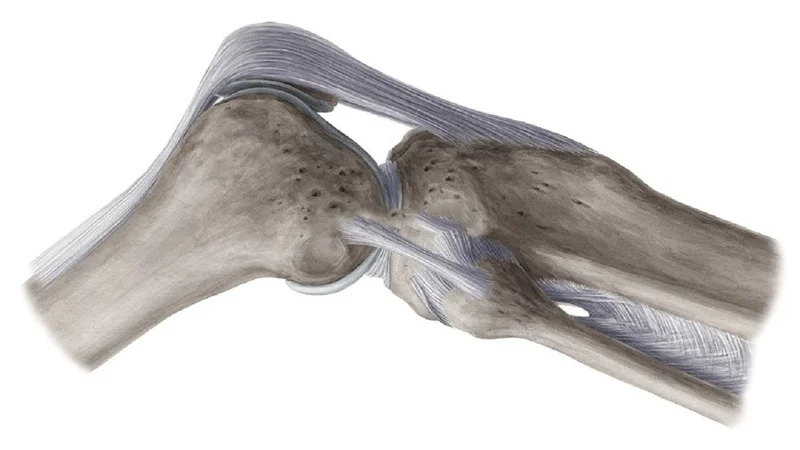
Elbow ligament
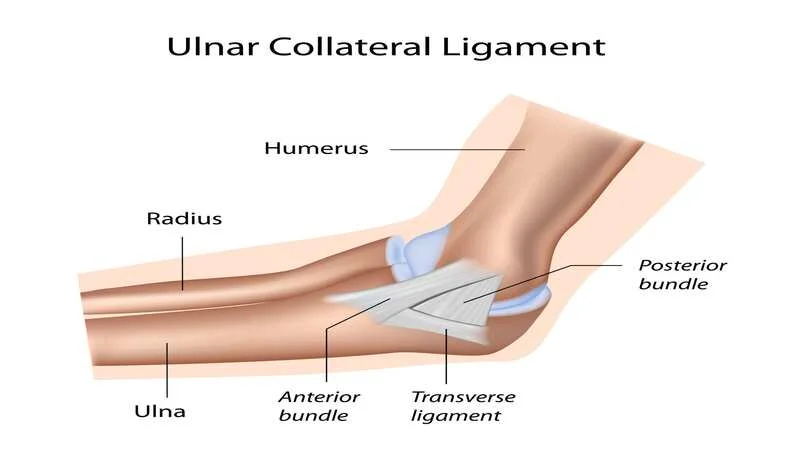
The elbow joint is a hinged joint formed by connecting the lower end of the humerus to the lower extremity (the lower bone of the forearm). The stability of the elbow joint depends on the inherent stability of the joint surfaces, the strong capsule, and the lateral ligaments.
The coronoid process is a major stabilizer of the elbow joint. In addition, it is the junction of the elbow ligament that forms the anterior protrusion of the alcranone and prevents posterior dislocation of the elbow. There are four ligaments around the elbow including:
- Ulnar Collateral Ligament (UCL): This ligament is attached to the lower zygomatic bone.
- Radial Collateral Ligament (RCL): This one connects the humerus to the outer bone of the forearm, called the radius.
- Annular ligament: it surrounds the top of the radius bone and holds it against the lower extremity.
Read More: What is gout? Cause and methods of treatment
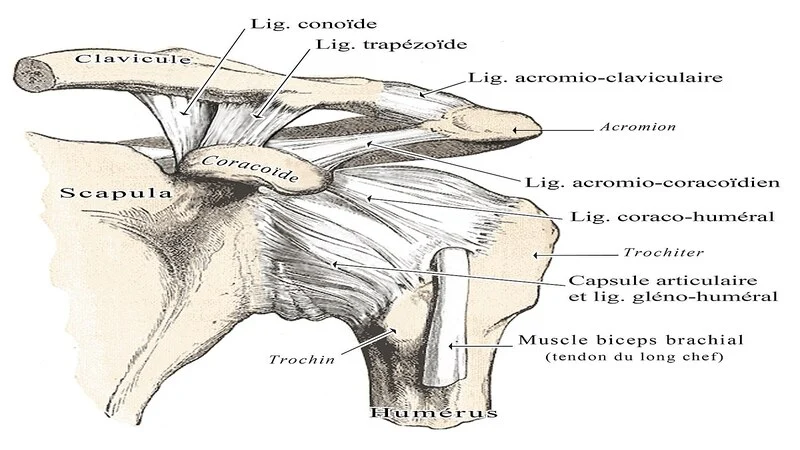
Shoulder ligament
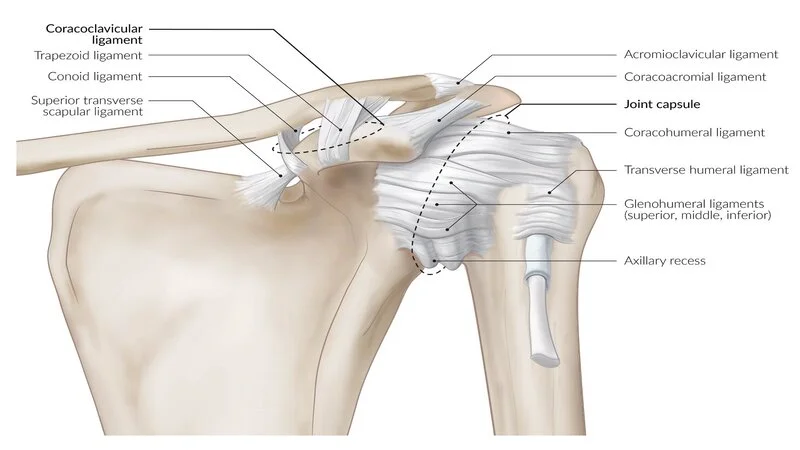
The ligaments in the shoulder connect the humerus to the shoulder blade or scapula. It also attaches the clavicle or collarbone to the top of the shoulder blade. When these ligaments are stretched, the shoulder becomes unstable. This is especially true for young people and athletes who put pressure on their shoulders. The shoulder ligament may also be twisted or torn by using the arm to restrain the fall.
Ankle ligament
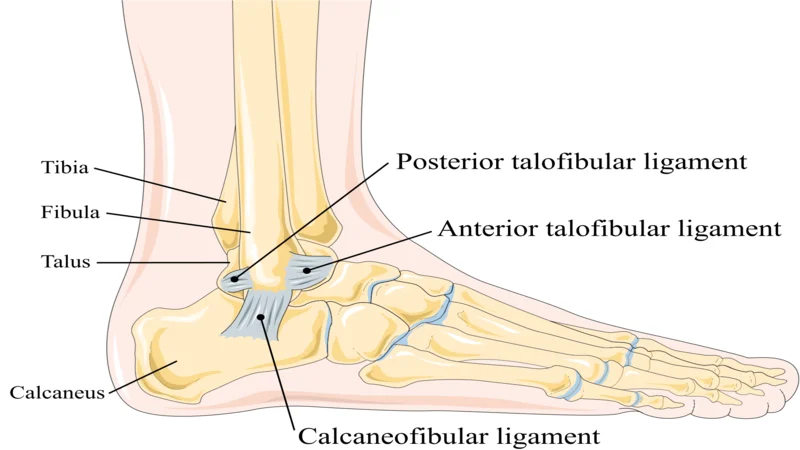
There are several ligaments around the ankle. The three main ligaments are located on the outside of the ankle. These ligaments include the “Anterior Talofibular” ligament, the “Posterior Talofibular” ligament, and the “Calcaneofibular” ligament. All three start in the fibula (thin) bone area.
The calcaneofibular bone ligament connects the large bone to the heel bone. The anterior and posterior talofibular ligaments connect the talus bone (the bone between the heel and the tibia) to the thin bone outside the ankle. However, the posterior talofibular ligament is located along the back of the ankle, and injuries to this ligament are not common.
The set of ligaments on the inside of the ankle is called the deltoid ligament. These ligaments act as lateral ligaments and, for extra support, attach a large bone to similar bones on the inside of the foot.
When the ankle is severely paralyzed, one of these ligaments ruptures. The most common torsion occurs when your foot rotates below the ankle. This usually happens during exercise, especially in jumping sports such as basketball. In fact, when you wrap your ankle, you usually damage one of these ligaments. To prevent all kinds of ligament injuries, knowing how to do sports correctly and learning the science of kinesiology are very effective.
Read More: Heel spurs, its diagnosis and treatment approaches
Wrist and thumb ligaments
There are 20 ligaments in the wrist that connect the different bones. Ligament rupture may occur in these areas as a result of falling on the outstretched hand. The scapholunate ligament and the triangular fibrocartilage ligament (TFCC) are the most important hand ligaments that are most likely to be damaged.
The lateral ligament of the ulnar (connecting the thumb to the zygomatic bone below the forearm) can rupture while skiing. This injury is often called a “skier’s thumb”. Accordingly, the thumb may be injured in difficult situations or when falling.
Neck and spine ligaments
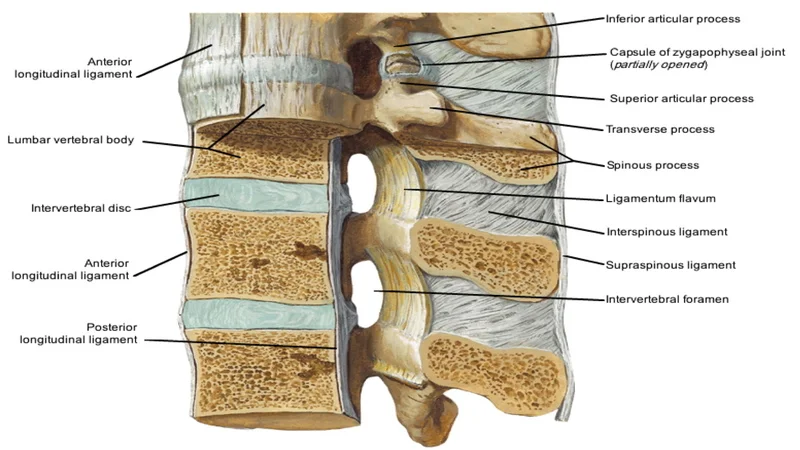
Spinal ligaments include the two upper parts of the shoulder in the neck area, known as the supra-shoulder ligaments. These ligaments help to bend the neck in different directions.
Also, the “nuchal ligament,” a fibrous membrane, is connected to the upper cervical ligaments. This ligament extends to the seventh cervical vertebra. Acceleration and sudden deceleration, such as heavy braking during accidents, cause severe cervical spine movement. It also increases the chance of rupture of the cervical ligaments.
The ligament system in the spine, along with the tendons and muscles, provides a natural protector to protect the spine and spinal cord from injury. Ligaments help stabilize the joint when resting and moving. It also prevents damage from excessive stretching and flexibility. These ligaments may be damaged when lifting very heavy objects.
What is a cruciate ligament, and how is it damaged?
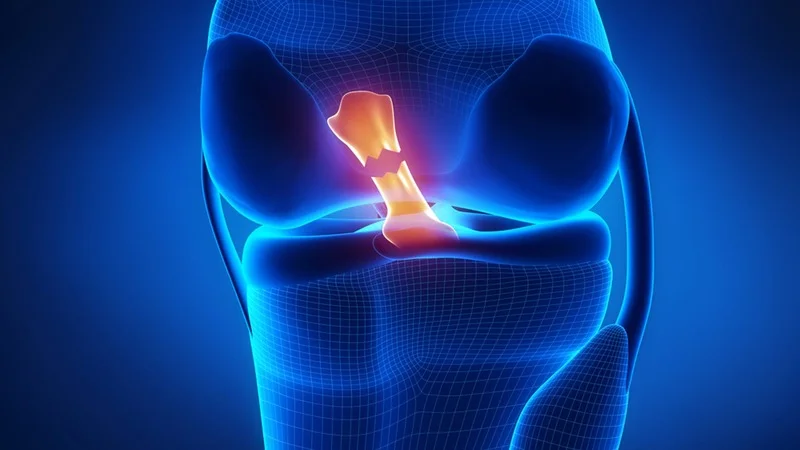
Cruciate ligaments are pairs of ligaments that are held together like the letter X. They are present in several joints of the body, such as the knee joint, the atlantoaxial joint (the joint between the first and second cervical vertebrae), and the fingers. These ligaments stabilize the joint in a ladder-like manner. These ligaments also allow for a wide range of motion.
In the knee joint, three bones are connected by ligaments: the femur, the tibia, and the patella. There are also ligaments on the back of the knee to protect the front of the joint. There are accompanying ligaments on the sides of the knee that act as strong ropes to hold the bones together and the knee in place.
The anterior and posterior cruciate ligaments are located in the inner part of the knee joint and cross each other to form an X-shape. These ligaments control the back and forth movement of the knee.
One of the most common knee injuries is a sprained or torn anterior cruciate ligament. Injury to the ACL ligament of the knee is usually more common during exercise that involves abrupt stopping or changing direction, jumping, and landing. For example, sports such as soccer, basketball, rugby, and downhill skiing increase the risk of injury.
Many people hear a loud noise when an anterior cruciate ligament injury occurs. Approximately half of these ligament injuries occur with damage to other knee structures such as articular cartilage, meniscus, or other ligaments.
Read More: What is arthroplasty? its advantages and disadvantages
Which joints are most vulnerable to ligament injury?
Although ligament injuries can occur in any joint in the body, they are more common in some areas. The most common sites of a ligament injury in the joints are:
Knee Joint
Rupture of the cruciate and lateral ligaments in the knee joint is usually caused by severe sports injuries. If the severity of these tears is high, they usually repair the damaged ligament to treat the instability.
Ankle
Injury to the lateral ligaments of the ankle, especially the external lateral ligament, usually results from torsion. Treatment for leg sprains is usually non-surgical and with a period of immobility. In cases where ankle instability is due to severe sprains and ligament injuries, the patient will need ligament reconstruction surgery.
If you need surgery, we suggest you go for treatment of an ankle ligament tear in Dubai. Dubai will provide you with the best doctors for your surgery. Moreover, patients come to find the treatment of tarsal coalition in Dubai. So, if you need some of these treatments, never forget to visit the best doctors in Dubai.
Shoulder
Rupture of the acromioclavicular ligament in the shoulder is usually treated surgically if it is associated with acromioclavicular joint dislocation and excessive displacement. In cases where the amount of dislocation and displacement of the acromion and clavicle bones is low, treatment with a period of shoulder immobility is recommended. However, in cases of chronic instability, the patient may need ligament reconstruction surgery.
Wrist
Severe stretching of the wrist causes damage to the ligaments between the bones. Treatment for these strains and ligament ruptures usually involves a period of immobilization of the wrist with a cast or brace. In cases where this ligament injury causes long-term instability, the patient may need surgery to repair the damaged ligaments.
Thumb
Severe stretching of the metacarpophalangeal joint of the thumb can rupture its lateral ligament. If this joint becomes unstable, the damaged ligament may need to be repaired.
Read More: What is an Achilles tendon and why is it damaged?
How to treat ligament injury?
Treatment for ligament injuries usually involves immobilizing the joint for several weeks. This immobility often causes the torn ligament to heal.
Torn ligaments are often in a way that does not allow repair. The ligament is shaved and crushed at the site of the rupture. In this condition, there is no place in the ligament for suturing.
Some ligament ruptures at the bone-ligament interface may only be treated surgically.
However, in most cases, the treatment is with joint immobility for a while. In this way, the tissue repairs itself spontaneously, and the joints begin to move to prevent dryness. These movements are performed in the form of stretching and strengthening exercises under the supervision of a physiotherapist.
If the joint remains unstable after these steps, it is clear that the damaged ligament hasn’t been able to heal effectively.
In this case, surgery will usually be needed. This surgery is no longer a repair but a reconstruction. Ligament repair is usually done a few months after the initial injury.
In reconstruction surgery, the damaged ligament isn’t usually repaired but replaced by another tissue to do the job. This replacement tissue is usually a tendon that is taken from another part of the body.
Due to the high tissue similarity between the ligament and the tendon, the tendon can be used instead of the ligament. In reconstructive surgery, a tendon graft is attached to the target bone in two directions. In this way, the tendon is placed in place of the previous ligament and does its job.
Note: There are so many doctors that will help you find the treatment of sesamoid injuries in Dubai. So, if you live in this city, or if you want to travel to Dubai for your medical issues, never forget to check for the best doctors.